Overview
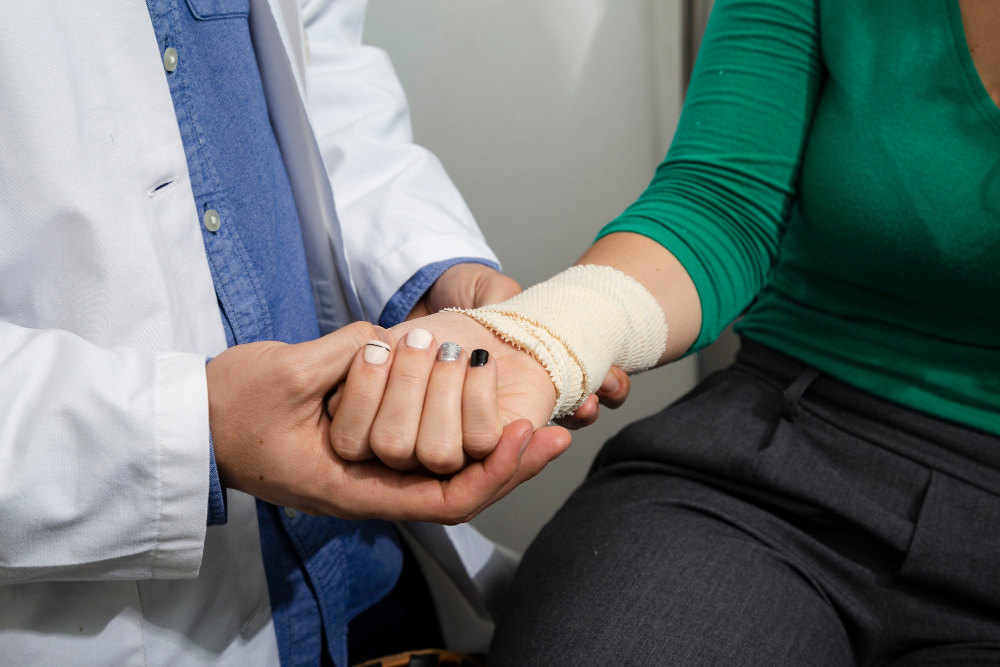
Trauma and fractures refer to injuries that result from accidents, falls, or other impactful events that cause bone damage or significant bodily harm. These injuries can vary in severity and often require immediate medical attention for diagnosis, treatment, and recovery.
Trauma and fractures can occur in various parts of the body, affecting bones, joints, and soft tissues. The nature of these injuries can range from minor fractures and sprains to more severe cases involving multiple fractures and complex trauma.
Common Causes and Types
Fractures occur when bones break due to excessive force or impact. They can be categorized into several types, including:
- Closed Fractures: The bone breaks but does not penetrate the skin.
- Open Fractures: The bone breaks and pierces through the skin, increasing the risk of infection.
- Hairline Fractures: Small, often hard-to-detect cracks in the bone.
- Comminuted Fractures: The bone shatters into multiple pieces.
- Greenstick Fractures: Common in children, where the bone bends but doesn't break completely.
- Stress Fractures: Tiny cracks in the bone's surface due to repetitive stress or overuse.
Trauma encompasses a wide range of injuries resulting from accidents, falls, and high-impact events, including:Motor Vehicle Accidents: Injuries from car, motorcycle, or pedestrian accidents.
- Sports-Related Injuries: Common in athletes, including sprains, fractures, and dislocations.
- Workplace Injuries: Occur in various industries, often due to slips, trips, and falls.
- Falls: Falls from heights or on the same level can result in fractures and trauma.
- Violence and Assault: Injuries resulting from physical altercations or criminal acts.
- Outdoor and Recreational Injuries: Common among hikers, climbers, and adventurers.
Treatment and Care:
- Initial Stabilization: In cases of severe trauma, ensuring the patient's safety and stability is a priority. This may involve immobilizing the injured area or administering immediate first aid.
- Diagnostic Imaging: X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans are used to assess the extent and nature of the injury.
- Reduction and Realignment: For fractures, the bone may need to be realigned or reduced, which can be done non-surgically or through surgical intervention.
- Casting and Immobilization: Many fractures are treated with casts or braces to immobilize the affected area and promote healing.
- Surgery: In complex fractures or trauma, surgery may be necessary to repair and stabilize the bones.
- Physiotherapy: Rehabilitation and physical therapy programs help patients regain strength, mobility, and functionality.
- Pain Management: Medications and therapies may be prescribed to manage pain and discomfort.
- Follow-Up Care: Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor healing progress and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
When to Seek Medical Attention
It's crucial to seek immediate medical attention for trauma and fractures when:
- There is severe pain, deformity, or an open wound at the site of injury.
- The injury is accompanied by numbness, tingling, or a lack of sensation in the affected area.
- There is an inability to move or bear weight on the injured body part.
- The injury involves the neck, head, spine, or pelvis, as these can be life-threatening.
Call +91 98412 98412 for medical emergencies or 044 2238 2248 / +91 98848 99091 to book an appointment.