Overview
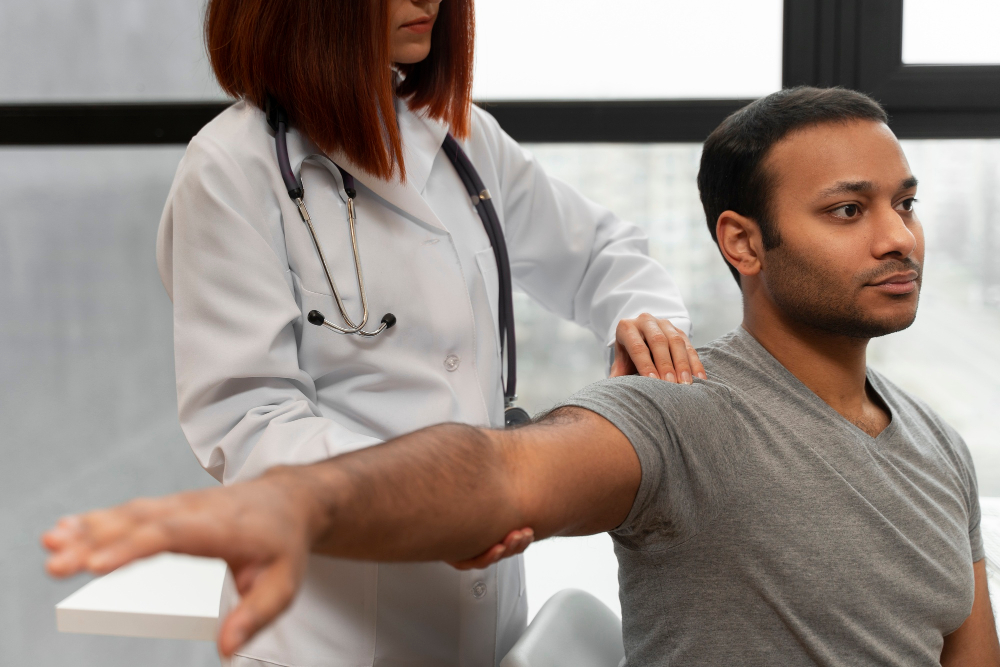
Shoulder and elbow pain refer to discomfort or pain experienced in the shoulder or elbow regions of the upper extremities. These areas are crucial for various daily activities and can be affected by a range of conditions and injuries.
The shoulder consists of a complex network of bones, joints, and muscles that allow for a wide range of motion. It's prone to pain and discomfort due to its mobility and frequent use. In contrast, the elbow is a hinge joint, and pain in this area can hinder activities that require bending or extending the arm.
Shoulder and elbow pain can manifest in several ways, including:
- Localized discomfort in the shoulder or elbow joint.
- Radiating pain that extends to the arm, hand, or even the neck.
- Stiffness, limiting the range of motion in the shoulder or elbow.
- Weakness or numbness in the affected arm.
The severity and duration of shoulder and elbow pain can vary, and it may be triggered or exacerbated by factors like overuse, poor posture, or underlying medical conditions. While mild pain can often be managed at home with rest and over-the-counter pain relief, severe or persistent pain may require medical evaluation and treatment. If your shoulder or elbow pain significantly impacts your daily life or mobility, seeking medical assistance at Parvathy Multispeciality Hospital in Chennai, is advisable.
Common Causes of Shoulder and Elbow Pain
- Muscular Strain: Overuse or strain of the muscles and tendons around the shoulder and elbow, often due to repetitive motions or heavy lifting.
- Rotator Cuff Injuries: Tears or inflammation of the rotator cuff tendons can lead to shoulder pain and limited mobility.
- Tendonitis: Inflammation of the tendons in the shoulder or elbow can result in pain, especially with specific movements.
- Arthritis: Conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis can affect the shoulder and elbow joints, causing chronic pain and stiffness.
- Fractures and Dislocations: Injuries such as fractures or dislocations in the shoulder or elbow can lead to acute pain and require medical attention.
- Nerve Compression: Pinched nerves or conditions like thoracic outlet syndrome can cause pain, numbness, or tingling in the shoulder and arm.
Treatment and Care:
- Physiotherapy: Physiotherapy programs aim to improve strength, flexibility, and the range of motion in the shoulder and elbow. Therapists use exercises, manual techniques, and modalities to reduce pain.
- Medications: Pain relievers, including over-the-counter and prescription medications, can help alleviate discomfort and reduce inflammation.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections may be administered into the affected area to reduce inflammation and provide relief.
- Surgery: Surgical interventions may be necessary for severe shoulder or elbow conditions that don't respond to conservative treatments. Common surgeries include rotator cuff repair, joint replacement, and arthroscopic procedures.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Improving ergonomics, posture, and daily habits can help prevent and manage shoulder and elbow pain. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and weight can reduce the risk of these issues.
- Bracing and Support: Orthopaedic braces or supports may be recommended to stabilize the shoulder or elbow and alleviate pain.
When to Consult a Doctor ?
Consult a doctor whenever you experience shoulder or elbow pain that affects your daily life. Additionally, seek medical attention if you experience:
- Persistent Pain: If your shoulder or elbow pain lingers and disrupts your everyday activities, consult a specialist.
- Limited Range of Motion: Difficulty in moving the shoulder or elbow as usual is a sign to consult a healthcare professional.
- Stiffness: Experiencing stiffness that hampers basic movements may indicate an underlying issue.
- Pain During Activity: Worsening pain during physical activities may be indicative of an injury or underlying condition that requires assessment.
- Pain at Rest: If pain persists even at rest, it could suggest an underlying problem.
- Recent Injury: In cases of recent trauma or injury affecting the shoulder or elbow, seek immediate medical care.
Call +91 98412 98412 for medical emergencies or 044 2238 2248 / +91 98848 99091 to book an appointment.
General (FAQ) For Shoulder and elbow
-
Rest: Allow your shoulder to rest and avoid activities that worsen the pain.
-
Ice: Apply ice to the affected area to reduce inflammation.
-
Compression: Use a compression bandage to support the shoulder.
-
Elevation: Elevate the arm to minimize swelling.
Treatment depends on the cause:
-
Rest and avoid activities that aggravate the pain
-
Ice application to reduce inflammation
-
Over-the-counter pain relievers
-
Physical therapy for rehabilitation
-
Medical consultation for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment
Causes include:
-
Overuse or repetitive motion
-
Tendonitis or bursitis
-
Elbow fractures or dislocations
-
Arthritis
-
Nerve compression
-
Sports injuries