Overview
Electrophysiology, often referred to as cardiac electrophysiology, is a specialized branch of cardiology that focuses on the electrical activities of the heart. It deals with the study and treatment of heart rhythm disorders, also known as arrhythmias. These conditions can range from benign to life-threatening, and electrophysiologists play a crucial role in diagnosing, understanding, and managing them.
The heart's electrical system is responsible for regulating the heartbeat, ensuring it beats at a steady rhythm and delivers oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. However, abnormalities in the heart's electrical pathways can lead to arrhythmias, which can cause symptoms like palpitations, dizziness, chest pain, or, in severe cases, sudden cardiac arrest.
The heart's electrical system is responsible for regulating the heartbeat, ensuring it beats at a steady rhythm and delivers oxygen-rich blood throughout the body. However, abnormalities in the heart's electrical pathways can lead to arrhythmias, which can cause symptoms like palpitations, dizziness, chest pain, or, in severe cases, sudden cardiac arrest.
Common Electrophysiology Procedures (Possible Interventions)
Electrophysiologists are highly specialized cardiologists who undergo additional training to become experts in understanding and treating heart rhythm disorders. They use a range of diagnostic and treatment modalities to address these conditions, ensuring that the heart's electrical system functions correctly.
Some common electrophysiology procedures and interventions include:
Some common electrophysiology procedures and interventions include:
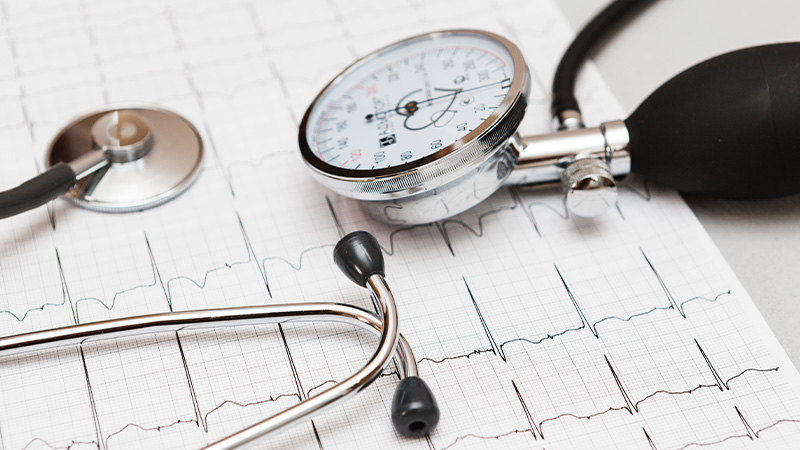
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): A non-invasive test that records the heart's electrical activity and helps diagnose arrhythmias and other heart conditions.
- Holter Monitor: A portable device that continuously records the heart's electrical activity over a 24-hour period or longer to detect intermittent arrhythmias.
- Event Monitor: A wearable monitor that patients can activate when they experience symptoms, helping to capture and diagnose arrhythmias.
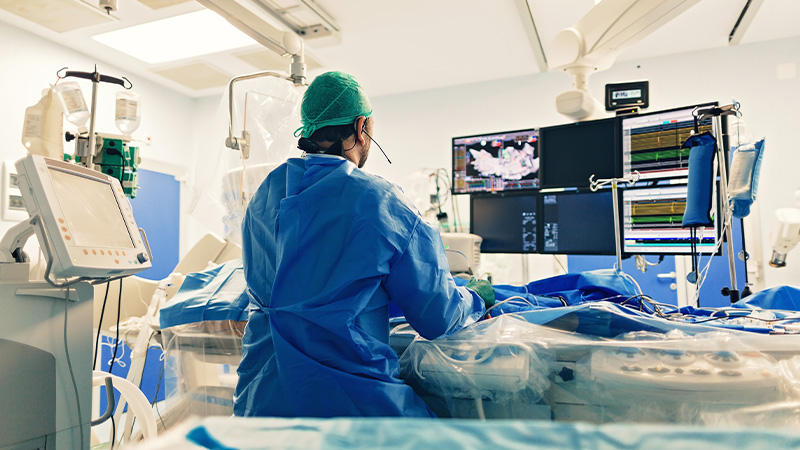
- Electrophysiology Study (EPS): Invasive testing involving the insertion of catheters into the heart to evaluate its electrical activity and pinpoint the source of arrhythmias.
- Catheter Ablation: A minimally invasive procedure in which a catheter is used to deliver energy to the heart tissue, creating scar tissue to block abnormal electrical pathways.
- Implantable Devices: The implantation of devices such as pacemakers, implantable cardioverter-defibrillators (ICDs), or cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) devices to regulate heart rhythms.
- Antiarrhythmic Medications: Prescription medications to control or prevent arrhythmias.
- Cardioversion: A procedure in which controlled electrical shocks are used to restore a normal heart rhythm.
- Implantable Loop Recorder: A small device implanted under the skin to monitor heart rhythms for extended periods.
Treatment and Care
Electrophysiologists provide a range of treatment options tailored to the specific arrhythmia, its underlying cause, and the patient's overall health.
These may include:
These may include:
- Medications: Prescription medications to control heart rhythm and rate, manage symptoms, and reduce the risk of complications.
- Catheter Ablation: A procedure to treat arrhythmias by destroying or isolating the abnormal heart tissue responsible for the condition.
- Implantable Devices: The placement of pacemakers, ICDs, or CRT devices to regulate heart rhythms and provide life-saving interventions when necessary.
- Lifestyle Modification: Guidance on lifestyle changes, such as reducing caffeine or alcohol intake, managing stress, and maintaining a heart-healthy diet.
- Follow-up Care: Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments to assess the effectiveness of treatment and make necessary adjustments.
When to Consult a Doctor ?
If you experience symptoms such as palpitations, dizziness, chest pain, or fainting spells, or if you have been diagnosed with an arrhythmia, it is advisable to consult an cardiac expert at Parvathy Institute of Cardiac Sciences, when:
- You require a definitive diagnosis of a heart rhythm disorder.
- Your condition is complex or difficult to manage, necessitating the expertise of a cardio expert.
- You are exploring treatment options for arrhythmias, including catheter ablation or implantable devices.
- You seek a second opinion or specialized care for arrhythmia-related concerns.
- You have a family history of heart rhythm disorders, and you are interested in preventive care or early intervention.
Call +91 98412 98412 for medical emergencies or 044 2238 2248 / +91 98848 99091 to book an appointment.
General (FAQ) For Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology is used to study and diagnose electrical activities in the heart. It helps identify and treat various heart rhythm disorders, also known as arrhythmias.
An electrophysiology procedure involves the use of catheters and specialized equipment to study the electrical signals in the heart. It helps diagnose and treat abnormal heart rhythms.
An electrophysiologist is a cardiologist who specializes in diagnosing and treating heart rhythm disorders. They use electrophysiology studies to assess the heart's electrical system and may perform procedures like ablation to correct rhythm issues.
While both involve the heart's electrical activity, they are different. Electrophysiology is a broader field, including procedures and studies to diagnose and treat heart rhythm issues. An Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a specific test that records the heart's electrical activity.
During electrophysiology studies, patients are typically under sedation or anesthesia, so they don't feel pain. After the procedure, some discomfort may occur at the catheter insertion site.
Electrophysiology procedures are usually considered minimally invasive and are not categorized as major surgeries. They involve catheter-based techniques rather than open-heart surgery.
Angiography involves imaging blood vessels, often using contrast dye, to assess blood flow. Electrophysiology focuses on studying the heart's electrical activity and treating rhythm disorders.
Yes, a pacemaker falls under the realm of electrophysiology. Electrophysiologists often implant pacemakers to regulate and control heart rhythms.
While electrophysiology procedures are generally safe, potential risks include bleeding, infection, and damage to blood vessels or the heart. Discuss any concerns with your electrophysiologist.
Electrophysiologists treat a range of heart rhythm disorders, including atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, ventricular tachycardia, and bradycardia. They also manage devices like pacemakers and defibrillators.